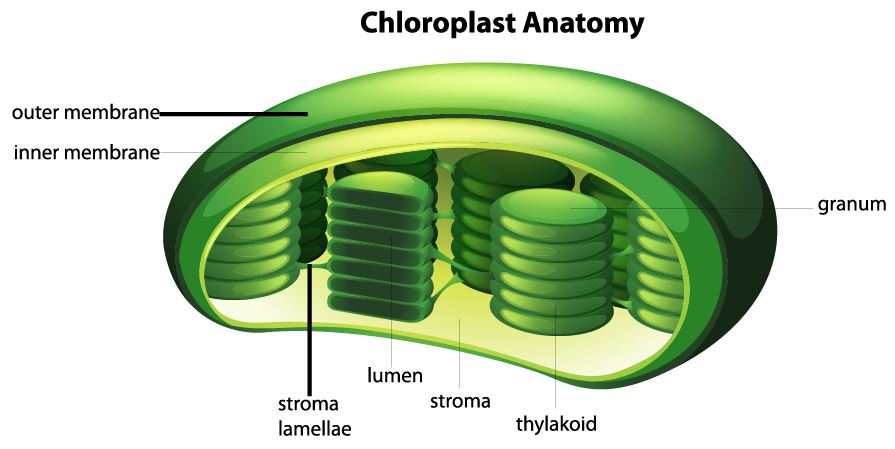
41 label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function
Chloroplast - Wikipedia A chloroplast / ˈ k l ɔːr ə ˌ p l æ s t,-p l ɑː s t / is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells.The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is ... Chloroplast Fact Sheet: Definition, Structure, Genome, and Function ... Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell by converting light energy of the sun into sugar that can be used by the cell. This entire process is known as photosynthesis and it all depends on the high concentration of chlorophyll, the molecule that absorbs light energy and gives plants and algae a green color.
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology: Plant Cell Structure - Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are one of several different types of plastids, plant cell organelles that are involved in energy storage and the synthesis of metabolic materials. The colorless leucoplasts, for instance, are involved in the synthesis of starch, oils, and proteins. Yellow-to-red colored chromoplasts manufacture carotenoids, and the green colored ...
Label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function
Cell Organelles- Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram A chloroplast is a type of plastic that is involved in photosynthesis in plants and algae. Chloroplast contains an essential pigment called chlorophyll necessary to trap sunlight for the production of glucose. Structure of Chloroplast. It is a double-membraned structure with its own DNA which is inherited from the previous chloroplast. Definition, Functions and Benefits - Biology Dictionary Chlorophyll Definition. Chlorophyll is a molecule produced by plants, algae and cyanobacteria which aids in the conversion of light energy into chemical bonds. Chlorophyll is known as a pigment, or molecule that reflects some wavelengths of light, while absorbing others. Pigments produce a variety of colors in the plant and animal world. Chloroplast: Structure and Function - Biology Wise The major components of a chloroplast are as illustrated and explained below. Envelope The chloroplast envelope is double-membrane structure comprising an outer and an inner membrane. Each of these membranes is a phospholipid bilayer, and is 6 - 8 nm thick. A 10 - 20 nm thick space present between the two membranes is known as intermembrane space.
Label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function. 5.1.1 Chloroplast Structures & their Functions - Save My Exams Chloroplasts are the organelles in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs Each chloroplast is surrounded by a double-membrane envelope Each of the envelope membranes is a phospholipid bilayer Chloroplasts are filled with a fluid known as the stroma The stroma is the site of the light-independent stage of photosynthesis Chloroplast Structure & Function Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Chloroplast Structure & Function. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Home. ... - 1st of many interconnected sac-like membranous disks within the chloroplasts - contains light absorbing pigments - contains molecules that absorb energy from the sun. ... What does label X identify? 4 ... Biology for Kids: Plant Cell Chloroplasts - Ducksters Chloroplasts are unique structures found in plant cells that specialize in converting sunlight into energy that plants can use. This process is called photosynthesis . Chloroplasts are considered organelles in plant cells. Organelles are special structures in cells that perform specific functions. The main function of the chloroplast is ... Chloroplasts- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram A chloroplast thus has the following parts: Envelope (Outer membrane) It is a semi-porous membrane and is permeable to small molecules and ions, which diffuses easily. The outer membrane is not permeable to larger proteins. Intermembrane Space
Chloroplast Function in Photosynthesis - ThoughtCo Photosynthesis occurs in eukaryotic cell structures called chloroplasts. A chloroplast is a type of plant cell organelle known as a plastid. Plastids assist in storing and harvesting needed substances for energy production. A chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. Chloroplast - Definition, Function and Structure - Biology Dictionary Function of Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are the part of plant and algal cells that carry out photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy to energy stored in the form of sugar and other organic molecules that the plant or alga uses as food. Photosynthesis has two stages. In the first stage, the light-dependent reactions occur. Structure of Chloroplast (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion 1. Chloroplasts (Figs. 295-296), responsible for the photosynthesis of the plants, are the characteristic features of the cells of green plants. ADVERTISEMENTS: 2. Around the chloroplast is present a double membrane envelope. 3. Each membrane of chloroplasst is 35 to 50 Å thick. 4. Many dark-coloured grana are present. chloroplast | Definition, Function, Structure, Location, & Diagram Chloroplasts are a type of plastid—a round, oval, or disk-shaped body that is involved in the synthesis and storage of foodstuffs. Chloroplasts are distinguished from other types of plastids by their green colour, which results from the presence of two pigments, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.
Chloroplasts Definition, Structure, Function and Microscopy The circular DNA of chloroplast is refered to as cpDNA and helps regulate how the organelle functions. Membrane Compared to other organelles, chloroplasts have three types of membranes that serve different functions. These include: The smooth outer membrane (outer envelope membrane) The smooth inner membrane (inner envelope membrane) What Is the Function of Chloroplasts? - Reference.com Chloroplasts belong to a group of cells called plastids, which store energy and help plants convert light energy into food. Chloroplasts contain pigmentation in the forms of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, which help absorb light that photosynthesis needs in order to occur. Chlorophyll is also responsible for making plants green. In Which Part of the Chloroplast Does Each Stage Occur? Photosynthesis takes place in the cell's chloroplast in two stages: the light stage and the dark stage. Each stage occurs in a different part of the chloroplast. In the light stage of photosynthesis, the chloroplast absorbs the light of the sun. This sets off a series of chemical reactions, beginning by converting the sunlight to chemical energy. Chloroplast Structure: Chlorophyll, Stroma, Thylakoid, and Grana Chloroplasts are the structural sites of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into food. A cell that resides in a plant leaf, for example, might have hundreds of chloroplasts that...
Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast The chloroplast structure consists of the following parts: Membrane Envelope It comprises inner and outer lipid bilayer membranes. The inner membrane separates the stroma from the intermembrane space. Intermembrane Space The space between inner and outer membranes. Thylakoid System (Lamellae) The system is suspended in the stroma.
Chloroplasts - Structure And Functions - A Level Biology Functions of Chloroplast Absorption of light energy and conversion of it into biological energy. Production of NAPDH2 and evolution of oxygen through the process of photosys of water. Production of ATP by photophosphorylation. NADPH2 and ATP are the assimilatory powers of photosynthesis.
parts of a chloroplast Flashcards | Quizlet parts of a chloroplast STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity thylakoid Click card to see definition 👆 A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy. Click again to see term 👆 1/6
science.docx - What's More Activity 1.1 Understanding the... One of the raw materials used by green plants during photosynthesis is the gas carbon monoxide. 2. Plants can store some of the food they manufacture as starch. 3. The tiny holes through which gases enter and exit leaves are called chloroplasts. 4. During photosynthesis, green plants manufacture a sugar called glucose. 5.
Chloroplast Quiz - PurposeGames.com The chloroplast converts sulight, water and carbon dioxide into sugar: stored energy. Find the parts. Image by user It'sJustMe in the Wikimedia Commons. This quiz has tags. Click on the tags below to find other quizzes on the same subject.
Chloroplast: Definition, Structure, Function & Examples - Study.com The role of chloroplasts in photosynthesis is mainly to contain most of the reaction during photosynthesis. The plant will pump water into the leaves, and the leaves will also absorb carbon...


Post a Comment for "41 label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function"